Polyester fabric material is a crucial part of the modern fabric industry on the planet earth. It provides you with its power, multi-purpose, and ease of maintenance. Knowing polyester is necessary as it will enable you to select the most suitable fabric in terms of comfort, performance, and sustainability. This guide provides you with all the information regarding its origin, composition and properties. You will also be informed about its manufacture, uses, strengths, and weaknesses. At the end you will learn how to identify, compare and choose the best polyester fabric to suit your needs.
Origin and Development of Polyester
Early research on polymers led to the discovery of polyester in the 1930s. Its development can be followed to DuPont, who commercialized it in the textile industry. With time, improvements were made in terms of its strength, dyeing quality and recyclability. Polyester became one of the most multi-purpose garments globally because of these inventions. You have big manufacturing hubs today in China, India and the United States. Every nation plays a role in ensuring the production of polyester which is affordable, long lasting and accessible. It keeps advancing to guarantee improved performance and sustainability in worldwide textile industries.

What is Polyester Fiber Made of? – Chemical Composition
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a powerful synthetic polymer that is converted into polyester fiber. It is produced by polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. During this reaction, the monomers are joined into long chains of molecules using heat and catalysts. These chains make polyester strong, flexible and wear resistant. The very close molecular shape is what makes it hold its shape and prevents wrinkles. What you have is a tough, stretchy, and versatile fiber that can be used in clothing, upholstery and in thousands of other industrial applications.

Polyester Textile Material – Stepwise Production Process
Step 1: Raw Materials
You begin with two primary components, ethylene glycol, and terephthalic acid. They both are petroleum-based such as ethylene and p-xylene. Strong polymer chains of polyester are built out of these compounds. Bio-based alternatives consisting of renewable plants can also be found today. They provide a more sustainable alternative that has less carbon effect.
Step 2: Polymerization
The first phase is the mixing of the raw materials in the presence of catalysts and heat. The polycondensation and the esterification reactions bond the monomers into long chains of the polymer. The result of this process is molten polyethylene terephthalate or PET. Temperature and pressure have to be controlled to be consistent. What is obtained is a spinable polymer of definite size and viscosity.
Step 3: Melt Spinning
You heated the PET and pushed it through little spinerets. The polymer streams are cooled and solidified to continuous filaments. This step determines the texture and thickness of the fiber. The filaments are stretched in a slight manner to enhance strength and uniformity. It is a process that provides smooth, durable fibers to be used in different textile applications.
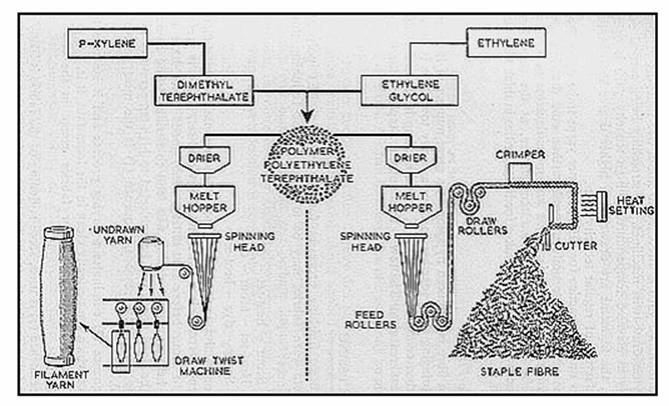
Step 4: Drawing and Texturing
You next squeeze the fibers to form straight protein chains. This step enhances tensile characteristics and elasticity. Then, you fiber-texture them with air-jet procedures or fake-twist. These methods produce crimped and thick shapes that look like natural yarns. They render polyester more user-friendly and flexible to a wide range of usages.
Step 5: Finishing
In completion, you color, weave, or knit the fibers into cloths. You can use flame-retardant, anti-static or waterproof coatings. Both treatments improve the performance and the look of the fabric. You may make finishes to accommodate clothing, upholstery, or technical fabrics.
Step 6: Variations and Efficiency
You cut filaments short and blend the staple fibers. Continuous filament yarns suit fabrics that are smooth and glossy. Polyester manufacturing requires a large amount of energy, approximately 100150 MJ/kg. Nevertheless, the current systems have adopted recycling as a closed loop to enhance efficiency and minimize waste.
Properties of Polyester
- Physical Properties: Polyester achieve great tensile strength of 4-9 g/denier. It has low stretch ability but regains shape fast after use. Wrinkles do not occur and the fiber dries quickly because of 0.4% water uptake.
- Chemical Properties: Polyester is good against acids, alkalis, mildew, and insects. Polyester is weak against strong bases and is distorted with high temperature. It is melted at around 260 O C and requires cautious ironing and washing.
- Thermal Properties: You feel good insulation when mixed with natural fibers. Polyester is easy to set in pleats. There are those that extinguish themselves, making garments less flammable.
- Optical and Aesthetic Properties: It is easy to dye it with disperse dyes to rich colors. Its sheen is dull to bright (according to finish). Frequent wear, however, may result in slight surface pilling.
- Durability Factors: Polyester offers high abrasion resistance to wear and tear. Its dimensional stability prevents the shrinkage or stretching of fabric. All these features render polyester suitable in long-lasting textile applications.
Types of Polyester Fibers
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET is the most widespread type of polyester fiber. It is commonly applied in clothing, furniture fabrics and plastic bottles. This fiber provides good strength, resistance to wrinkling and fast drying. PET can be counted on to provide dependable performance and simple maintenance. It is versatile and can be used in the fashion and industrial world.

Poly-1, 4-Cyclohexylene-Dimethylene Terephthalate (PCDT)
PCDT polyester is more elastic and flexible than the PET. You may apply it on stretch fabrics such as sportswear and mixed textile. Even after repeated washing, it does not shrink and retains its shape. The softness of PCDT and its recovery properties make it suitable in comfortable and durable clothes.

Other Variants
You may consider using bio-polyester derived out of vegetal sources so that it can be eco-friendly. Cationic dyeable polyester has the advantage of being colored easily in vivid colors that are permanent. Flame retardant polyester provides extra security in upholstery and protective clothing.
Fiber Forms and Specialized Types
Polyester strands come in the form of staple, filament, microfiber and textured yarns. Staple fibers can be used in cotton-like combinations and filament yarns in smooth finishes. Microfiber provides softness and moisture control, and textured yarn provides bulk. Polyester is used to make industrial fabrics stronger and low-pill varieties are used in industrial fabrics to make them last longer.
Application of Polyester Fiber in Textiles
- Clothing: Polyester is also used in daily clothes such as shirts, pants, and dresses. It maintains form easily and does not wrinkle when in use. It has a quick-drying and moisture-wicking feature in sports apparel to provide comfort. Polyester fleece and jackets are warm and durable in outer wear. It is very versatile and this makes it perfect in fashion and performance clothing.
- Home Furnishings: Polyester is used in curtains, upholstery, bedding, and carpets. It is stain resistant, does not fades, and wear out. The cloth does not lose its color or shape even after several washes. It is also soft and can be mixed with other fibers. This renders it ideal with permanent home decor materials.
- Industrial and Technical: Polyester can be trusted in terms of ropes, conveyor belts, and geotextiles. It is not easily stretchable and is good in mechanical stress. Polyester is also used in medical fabrics such as crafts and filters to give them strength. In car interiors, it offers strength and beauty. Its stability guarantees a good performance in harsh environments.
- Blends: Polyester-cotton blends are good at combining breathability with wrinkle resistance. Garments made of polyester-wool blends are more warm and structured. All blends provide versatility to various climates and applications. You have the option of softness, strength, or ease of maintenance. These combinations increase the selection of fabrics used in versatile textile use.
- New applications: You will find polyester in smart clothes with sensors. Reform polyester is used to encourage sustainable fashion and environmentally friendly manufacturing. It minimizes waste and ensures quality and performance. It is applied by brands in order to foster responsible and ethical innovation. These applications create the future of sophisticated textile design.
Comparison Table: Polyester vs Other Common Textile Materials
| Property | Polyester | Cotton | Nylon | Wool |
| Origin | Synthetic | Natural | Synthetic | Natural |
| Tensile Strength (g/denier) | 4-9 | 3-5 | 4-9 | 1-2 |
| Moisture Absorption (%) | 0.4 | 7-11 | 4-5 | 13-18 |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Excellent | Moderate |
| Cost | Low | Medium | High | High |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable | Biodegradable | Non-biodegradable | Biodegradable |
| Common Uses | Apparel, upholstery, sportswear | Clothing, towels, bedding | Activewear, ropes | Sweaters, coats, blankets |
Advantages of Polyester
- Polyester is very durable and resilient and this means that the garments can be washed and worn frequently.
- Its ability to resist wrinkling and shrinking allows you to have a clean smooth look with minimum effort.
- Your polyester is easy to iron or handle, as it does not need much ironing or special handling.
- The material is fast-drying and easily wicks, which keeps you cool and comfortable all day long.
- Polyester is also affordable, costing less than natural fibers and it performs remarkably well at a relatively low cost.
- It produces stable colors and durable prints so that your clothes do not lose color after several washes.
Disadvantages of Polyester
- Polyester is not breathable as natural fibres and it traps heat and makes wearing uncomfortable.
- It can hold body smells, particularly during the wet season, and this can be unpleasant to the smell.
- As a non-biodegradable substance, it contributes to the world waste and contaminates the water body with microplastic.
- The material accumulates statical energy rapidly, drawing in lint and dust and decreasing the comfort level in general.
- Polyester does not absorb a lot of moisture and therefore cannot be used on long wear in hot weather.
- The long usage can lead to skin irritation to sensitive users because of poor ventilation.
- Its artificial shine may seem not natural, which is not desirable in high-end or formal clothes.
Choosing the Right Polyester Fabric
Assess the Fabric Texture
Feel the cloth in your hand. A daily wear surface is best a smooth or soft one. Use a more coarse upholstery or high-wear surfaces. The weave and finish should be checked to be comfortable and strong. A fine weave is flexible, whereas a tighter weave is durable.
Assess the Fabric Thickness
Choose lightweight polyester to wear on the summer and sportswear. Select home furnishings and curtains in medium weight. Heavy fabrics can be used in upholstery or outer wear where durability is important. Always combine use with thickness to strike a balance between comfort and longevity. Polyester makes things thicker, whereas thin fabric is airy and flexible.
Consider the Blend Ratio
Polyester-cotton blends are more breathable and soft to wear on an everyday basis. Polymers Polyester-wool mixtures provide warmth and wrinkle resistance in winter garments. Know the influence of blend ratios on texture, weight, and care requirements. The correct combination guarantees comfort and better life. Always look at blend labels prior to buying.
Examine the Fabric Finish
Find special finishes that suit you. Sportswear is helped by moisture-wicking, and anti-static suits are used indoors. Natural glossy finishes are used to complement fashion clothes, and matte ones to complement interiors. Select test colorfastness and pilling. Good finish enhances aesthetic and increases life.
Correlate Fabric with Its Use
Use lightweight and breathable polyester in sportswear and casual wear. Use heavy, tough polyester on upholster or curtains. Stretch polyester suits are activewear where flexibility is required. To be used in various ways, choose balanced performance fabrics. Always categorize properties into the ultimate use of the fabric.
Conclusion
Polyester is among the dependable and versatile materials in contemporary fabrics. You can take advantage of its sturdiness, flexibility and low cost in a myriad of uses. Knowing polyester makes you make better decisions when it comes to fashion and functionality. Its active innovation, recycled fibers to environmentally friendly substitutes, promotes sustainable textile development. Although it has excellent performance, it is important to take care about its environmental impact. When you wear high-quality polyester or recycled polyester, you are supporting responsible manufacturing and durability of each piece of fabric you wear.
FAQs
Is polyester synthetic?
Yes, polyester is a synthetic fiber made from petroleum-derived polymers. It is created through chemical polymerization, not from natural sources.
Is polyester bad for you?
Polyester itself is not harmful when used in clothing or fabrics. However, it can trap heat and moisture, which may cause discomfort or irritation for sensitive skin.
Is polyester waterproof?
Polyester is water-resistant but not fully waterproof. It repels light moisture well, but water can pass through under heavy or prolonged exposure unless coated or treated.